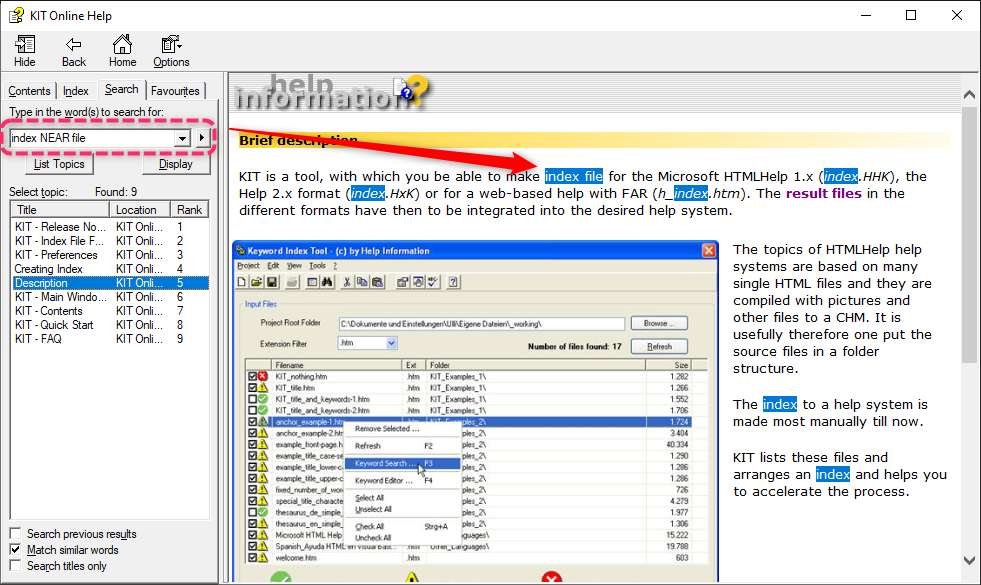
Search for a word or phrase in CHM files
In a single topic if you click the topic pane and then press CTRL+F, you can display a Find dialog box and search for a word or phrase in the current topic. Having a Search button you can use Full Text Search with the help viewer.
 |
|---|
| HTMLHelp Viewer - CHM Full Text Search |
A basic search of topics consists of the word or phrase you want to find. You can use wildcard expressions, nested expressions, Boolean operators, similar word matches, the previous results list, or topic titles to refine your search.
For a single compiled help (.chm) file, results are ranked by the number of hits within each topic (the number of times the search term is found within a topic). For a multiple-title help system, it's a little more complex.
If you have, for example, 5 compiled help files in your help system, the top-ranking hit from each title will be listed, followed by the second-ranking hit for each title, followed by the third, and so on. This process is followed until all the results are returned, or a total of 500 topic titles are listed.
To perform a full-text search
- In the navigation pane, click the Search tab and then type the word or phrase you want to find. Use the right-arrow button to add Boolean operators to your search.
- Click List Topics. Your search will return the first 500 hits. If you want to sort the topic list, click Title, Location, or Rank.
- Highlight the topic you want, and then click Display. (Alternatively, you can display any topic by double-clicking it.)
To refine a full-text search
You can refine a basic search by using wildcard expressions, nested expressions, and Boolean operators. You can also search only on the previous results list, request similar word matches, or search only the titles of topics in the table of contents.
- To refine a search to include just the last group of topics you searched, select the Search previous results check box.
-
To match similar spellings in a full-text search, select the Match similar words check box. When Match similar words is selected, the viewer matches minor grammatical variations of the word or phrase you entered, as well as the word or phrase itself. For example, if you entered "add" and selected this box, the Library viewer would find "add", "adds", and "added". This option is independent of other options or syntax. If you do a titles-only search, variations in titles will be matched. If you use quotes (or any other query operator) any variation of the word can appear; for example, "stemmed search" will also match "stemming search".
-
To search for words in document titles only, select the Search titles only check box.
To highlight words in searched topics
When searching for words in Help topics, you can specify that each occurrence of the word or phrase you searched for is highlighted in the topics that are found.
- On the Viewer toolbar, click View and then click Highlights to add a checkmark to this option to highlight all instances of the word or phrase.
- On the Viewer toolbar, click View and then click Highlights to remove the checkmark from this option and to turn off this feature.
Search Syntax
The basic rules for formulating queries are as follows:
- Searches are not case-sensitive, so you can type your search in uppercase or lowercase characters.
- You can search for any combination of letters (a--z) and numbers (0--9). You cannot search for single letters (a, b, c, etc.) and the following reserved words: an, and, as, at, be, but, by, do, for, from, have, he, in, it, not, of, on, or, she, that, the, there, they, this, to, we, which, with, you.
- Punctuation marks such as the period (.), colon (:), semicolon (;), comma (,), and hyphen (-) are ignored during a search.
- Group the elements of your search using "double quotes" or (parentheses). You cannot search for quotation marks.
*Note *If you are searching for a filename with an extension, you should group the entire string in double quotes ("filename.ext"). Otherwise, the search will treat the period as an OR operator.
Words, Phrases, and Wildcards
You can search for words or phrases and use wildcard expressions. The table below describes the results of these different kinds of searches.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| A single word | Select | Topics that contain the word "select." (You will also find its grammatical variations, such as "selector" and "selection".) |
| A phrase | "new operator" –or– 'new operator' |
Topics that contain the literal phrase "new operator" and all its grammatical variations. Without the quotation marks, the query is equivalent to specifying a new AND operator, which will find topics containing both of the individual words, instead of the phrase. |
| Wildcard expressions | Esc* | Topics that contain the terms "ESC," "escape," "escalation," and so on. The asterisk cannot be the only character in the words. |
| 80?86 | Topics that contain the terms "80186," "80286," "80386," and so on. The question mark cannot be the only character in the term. | |
| *86 | Topics that contain the terms "386," "486," "x86," "QEMM386," "8086," and so on. |
Operators: AND, OR, NOT, and NEAR
The AND, OR, NOT, and NEAR operators allow you to refine your search. The following table shows how to use each of these operators.
| Search for | Example | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Both terms in the same topic | dib AND palette –or– dib & palette |
Topics containing both the words "dib" and "palette." |
| Either term in a topic | raster OR vector –or– raster | vector |
Topics containing either the word "raster" or the word "vector." |
| The first term without the second term | ole NOT dde –or– ole ! dde |
Topics containing the word "OLE," but not the word "DDE." |
| Both terms in the same topic, close together | user NEAR kernel | Topics containing the word "user" within eight words of the word "kernel." |
Rules for Nested Expressions
The basic rules for searching topics using nested expressions are as follows:
- You can use parentheses to nest expressions within a query. The expressions in parentheses are evaluated before the rest of the query.
- If a query does not contain a nested expression, it is evaluated from left to right. For example, "Control NOT active OR dde" finds topics containing the term "control" without the term "active", or topics containing the term "control" and not "dde". (On the other hand, "control NOT (active OR dde)" finds topics containing the term "control" without either of the terms "active" or "dde".)
- Nesting allows you to create more complex search expressions. For example, "control AND ((active OR dde) NEAR window)" finds topics containing the term "control" along with the terms "active" and "window" close together, or containing "control" along with the terms "dde" and "window" close together.
- You cannot nest expressions more than five levels deep.